Hydroxypropyl beta-cyclodextrin: A multifunctional "molecular capsule" in coatings, driving green upgrades
Time:
Jul 04,2025
Hydroxypropyl beta-cyclodextrin ( HP-β-CD ) is one of the most water-soluble and widely used modified derivatives in the cyclodextrin family. In the coatings field, due to its unique molecular inclusion ability and excellent compatibility, it is becoming an important functional additive for improving coating performance and achieving environmentally friendly functions. The following are its specific applications, mechanisms of action, and advantages in coatings:
I. Main Application Areas
1. VOC and odor control
- Application method: Hydroxypropyl beta-cyclodextrin is directly added to the coating formulation (both water-based and solvent-based are possible, water-based is more common), the dosage is usually / 0.2%~3% (mass fraction). (质量分数)。
- Target:
- Includes residual monomers (such as styrene, acrylates).
- Captures curing by-products (such as aldehydes, amine odor molecules).
- Effect: Significantly reduces the VOC release and pungent odor of the coating film after construction, meeting green building standards (such as LEED 、 WELL ).
2. Functional additive slow release
- Application method:
- Pre-inclusion technology: First, the HP-β-CD is formed into an inclusion complex with bactericides, fungicides, fragrances, corrosion inhibitors, etc., and then dispersed into the coating.
- Direct addition: Using HP-β-CD dynamic inclusion of functional molecules in the coating.
- Effect:
- Protection of active ingredients (UV / oxidative degradation).
- Extended shelf life (e.g., antibacterial coatings release bactericides for months).
- On-demand release (humidity increase triggers fungicide release).
3. Formaldehyde capture and purification
- Application method: Add 1%~5% HPBCD to interior wall coatings.
- Mechanism:
- Hydrophobic cavity physically adsorbs formaldehyde.
- The hydroxyl group of hydroxypropyl undergoes acetalization reaction with formaldehyde (requires acid catalysis).
- Effect: Long-term decomposition of free formaldehyde indoors (e.g., purification coatings claim “formaldehyde removal rate”). >90%”)。
4. Improve compatibility and stability
- Application: Include hydrophobic additives (such as silane coupling agents, silicone leveling agents).
- Effect:
- Prevent phase separation.
- Improve the storage stability of coatings (especially water-based systems).
5. Film formation and plasticization assistance
- Mechanism: The hydroxypropyl chain of hydroxypropyl beta-cyclodextrin provides flexibility, slightly reducing the glass transition temperature of the coating film ( Tg ).
- Effect: Improve low-temperature film-forming properties and reduce the amount of film-forming aids.
II. Core mechanism of action: Molecular inclusion (host-guest chemistry)
- Structural advantages:
- Cavity size: HPBCD The inner diameter of the cavity is about 0.78 nm , perfectly matching small molecules such as benzene rings and heterocycles (such as formaldehyde, benzene).
- Surface modification: Hydroxypropyl substituents greatly improve water solubility ( >50 g/100mL water), preventing the precipitation of natural β - cyclodextrin.
- Low toxicity: LD ₅₀ > 2000 mg/kg (oral, rat), meets environmental requirements.
- Dynamic inclusion process:
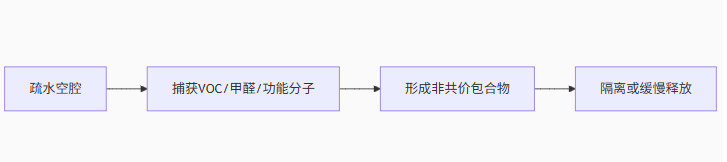
Through hydrophobic interactions, van der Waals forces and hydrogen bonds, the guest molecules are “locked” in the cavity, achieving:
- Shielding activity (such as reducing the corrosiveness of bactericides).
- Controlled release (environmental stimulus response).
Relevant News
Nov 25,2025
